Early-life inflammation promotes depressive symptoms in adolescence via microglial engulfment of dendritic spines
Release time:2023-02-07
Hits:
- Impact Factor:
- 18.68
- Journal:
- Neuron
- Abstract:
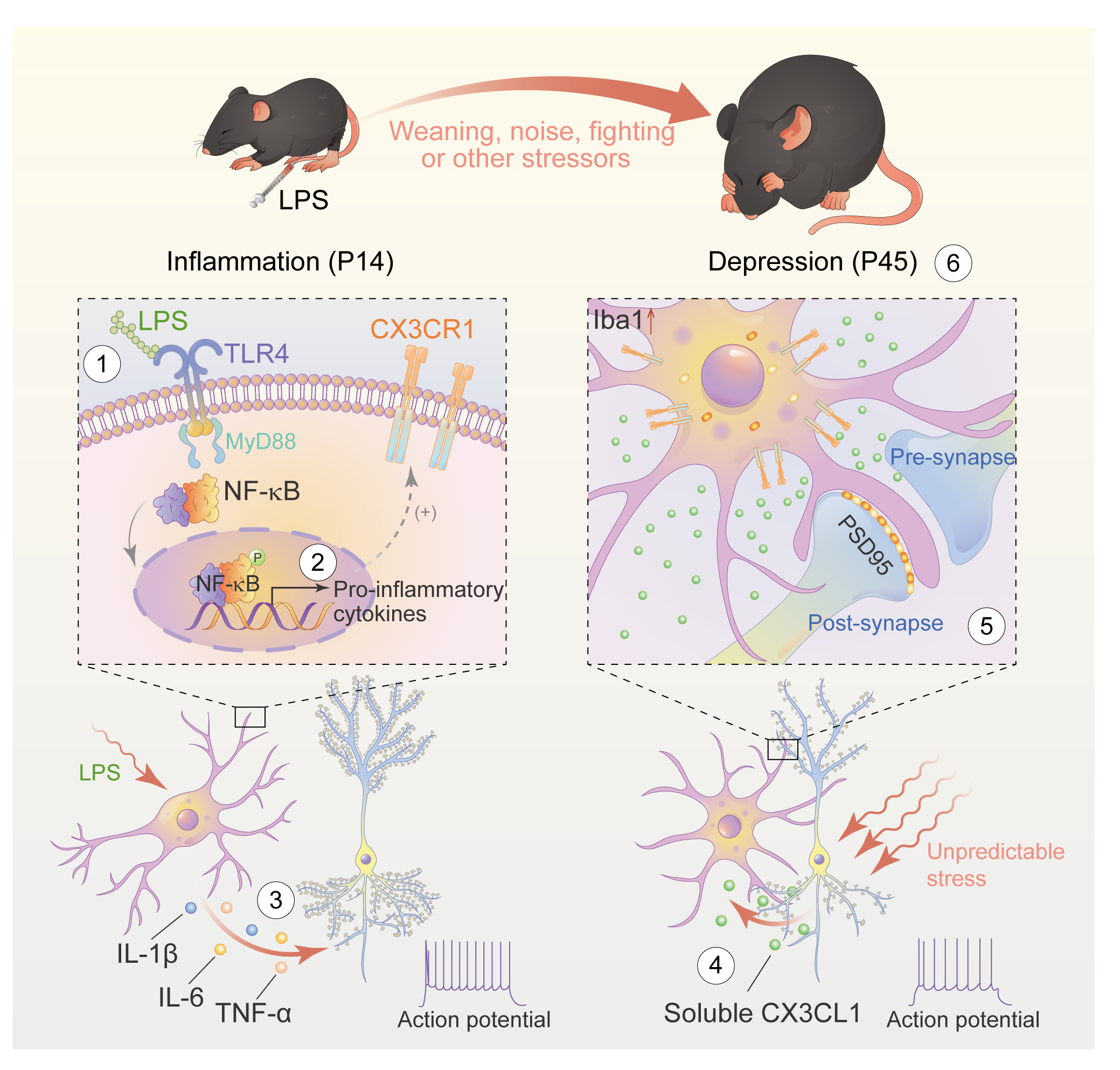
- Early-life inflammation increases the risk for depression in later life. Here, we demonstrate how early-life inflammation causes adolescent depressive-like symptoms: by altering the long-term neuronal spine engulfment capacity of microglia. For mice exposed to lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation via the Toll-like receptor 4/NF-κB signaling pathway at postnatal day (P) 14, ongoing longitudinal imaging of the living brain revealed that later stress (delivered during adolescence on P45) increases the extent of microglial engulfment around anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) glutamatergic neuronal (ACCGlu) spines. When the ACC microglia of LPS-treated mice were deleted or chemically inhibited, the mice did not exhibit depressive-like behaviors during adolescence. Moreover, we show that the fractalkine receptor CX3CR1 mediates stress-induced engulfment of ACCGlu neuronal spines. Together, our findings establish that early-life inflammation causes dysregulation of microglial engulfment capacity, which encodes long-lasting maladaptation of ACCGlu neurons to stress, thus promoting development of depression-like symptoms during adolescence.
- Note:
- 2021年度中国神经科学重大进展; Cell出版社年度中国最佳论文; 国际同行专家Neuron同期评述(Previews); ESI高被引论文(324次,2026.1.28)
- First Author:
- Peng Cao#, Changmao Chen#, An Liu#
- Co-author:
- Qinghong Shan, Xia Zhu, Chunhui Jia, Xiaoqi Peng, Mingjun Zhang, Zahra Farzinpour, Wenjie Zhou, Haitao Wang, Jiang-Ning Zhou, Xiaoyuan Song, Liecheng Wang, Wenjuan Tao, Changjian Zheng, Yan Zhang, Yu-Qiang Ding
- Indexed by:
- Journal paper
- Correspondence Author:
- Yan Jin*, Lin Xu*, Zhi Zhang*
- Volume:
- 109
- Issue:
- 16
- Page Number:
- 2573-2589
- Translation or Not:
- no
- Date of Publication:
- 2021-06-07
- Included Journals:
- SCI

 Login
Login
