Cui Hua

|
- Professor
- Supervisor of Doctorate Candidates
- Supervisor of Master's Candidates
- Name (English):Hua Cui
- Name (Pinyin):Cui Hua
- E-Mail:
- Business Address:环境资源楼-339
- Contact Information:0551-3600730
- Degree:Dr
- Professional Title:Professor
- Teacher College:Chemistry and Materials Science
 Contact Information
Contact Information
- Fax:
- OfficePhone:
- Email:
- Paper Publications
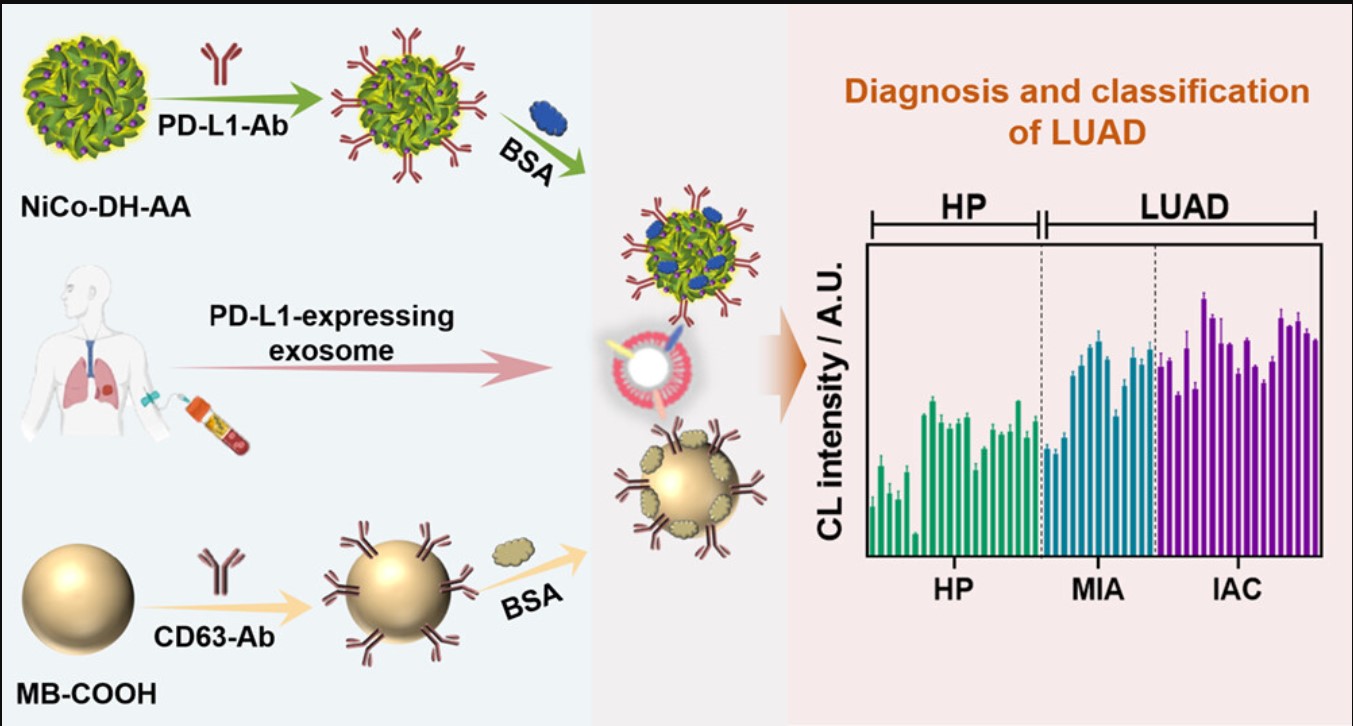
Ultrasensitive PD-L1-Expressing Exosome Immunosensors Based on a Chemiluminescent Nickel–Cobalt Hydroxide Nanoflower for Diagnosis and Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma
Release time:2024-07-09 Hits:
- DOI number:10.1021/acssensors.4c00954
- Journal:ACS Sens.
- Abstract:Programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1)-expressing exosomes are considered a potential marker for diagnosis and classification of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). There is an urgent need to develop highly sensitive and accurate chemiluminescence (CL) immunosensors for the detection of PD-L1-expressing exosomes. Herein, N-(4-aminobutyl)-N-ethylisopropanol-functionalized nickel–cobalt hydroxide (NiCo-DH-AA) with a hollow nanoflower structure as a highly efficient CL nanoprobe was synthesized using gold nanoparticles as a “bridge”. The resulting NiCo-DH-AA exhibited a strong and stable CL emission, which was ascribed to the exceptional catalytic capability and large specific surface area of NiCo-DH, along with the capacity of AuNPs to facilitate free radical generation. On this basis, an ultrasensitive sandwich CL immunosensor for the detection of PD-L1-expressing exosomes was constructed by using PD-L1 antibody-modified NiCo-DH-AA as an effective signal probe and rabbit anti-CD63 protein polyclonal antibody-modified carboxylated magnetic bead as a capture platform. The immunosensor demonstrated outstanding analytical performance with a wide detection range of 4.75 × 103–4.75 × 108 particles/mL and a low detection limit of 7.76 × 102 particles/mL, which was over 2 orders of magnitude lower than the reported CL method for detecting PD-L1-expressing exosomes. Importantly, it was able to differentiate well not only between healthy persons and LUAD patients (100% specificity and 87.5% sensitivity) but also between patients with minimally invasive adenocarcinoma and invasive adenocarcinoma (92.3% specificity and 52.6% sensitivity). Therefore, this study not only presents an ultrasensitive and accurate diagnostic method for LUAD but also offers a novel, simple, and noninvasive approach for the classification of LUAD.
- First Author:王慢莉
- Co-author:Shengnian Zhou,郑可颖,张文灿,王依莎
- Indexed by:Journal paper
- Correspondence Author:Dongliang Yang,shujiangnan,Hua Cui
- Discipline:Natural Science
- Document Type:J
- Volume:9
- Issue:6
- Page Number:3444–3454
- Translation or Not:no
- Date of Publication:2024-06-07
- Included Journals:SCI
- Links to published journals:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acssensors.4c00954