崔华
开通时间:..
最后更新时间:..
点击次数:
影响因子:6.215
DOI码:10.1016/j.electacta.2014.01.098
发表刊物:Electrochimica Acta
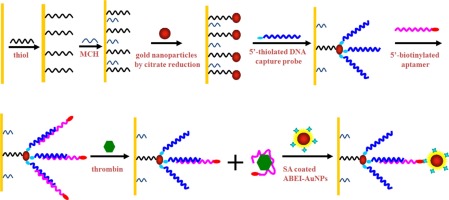
摘要:An electrochemiluminescence (ECL) bioassay was developed for the sensitive and selective detection of thrombin, based on dynamic interaction of aptamer, thrombin and N-(aminobutyl)-N-(ethylisoluminol) (ABEI) functionalized gold nanoparticles (ABEI-AuNPs). Gold nanoparticles by citrate reduction (AuNPs) were firstly assembled onto a gold electrode through 1, 3-propanedithiol, which was further connected with thiolated DNA capture probe. Then biotinylated DNA aptamer probe was assembled onto the modified electrode through the hybridization between capture probe and aptamer probe. After adding target thrombin, aptamer could bind tightly to target molecules to form a tertiary target–aptamer complex with a binding constant greater than DNA duplex, leading to partial extrication of biotinylated DNA aptamer probe from the surface of electrode. Finally, the ABEI-AuNPs coated with streptavidin (SA) were connected with the biotinylated DNA aptamer probe left after specific binding with thrombin to form the aptamer-ABEI-AuNPs complex on the electrode. When a double-step potential was applied to the electrode, an ECL signal was generated and recorded. The decrease of ECL signal was in proportion to the concentration of thrombin over the range of 1.0 × 10−12–1.0 × 10−9 M with a detection limit of 3.8 × 10−13 M. The proposed bioassay for the determination of thrombin is sensitive, specific, simple and fast. Finally, being challenged in real blood sample, the proposed bioassay was confirmed to be a good prospect for the detection of thrombin. This work provides a new way to design aptamer-based protocols for the determination of biologically important substances.
第一作者:于秀霞
论文类型:期刊论文
通讯作者:崔华
论文编号:000335424300019
学科门类:理学
文献类型:J
卷号:125
页面范围:156-162
ISSN号:0013-4686
是否译文:否
发表时间:2014-04-10
收录刊物:SCI
发布期刊链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0013468614001777