Cui Hua

|
- Professor
- Supervisor of Doctorate Candidates
- Supervisor of Master's Candidates
- Name (English):Hua Cui
- Name (Pinyin):Cui Hua
- E-Mail:
- Business Address:环境资源楼-339
- Contact Information:0551-3600730
- Degree:Dr
- Professional Title:Professor
- Teacher College:Chemistry and Materials Science
 Contact Information
Contact Information
- Fax:
- OfficePhone:
- Email:
- Paper Publications
Dissolved oxygen-induced highly efficient chemiluminescence of acridinium sulfonamide-functionalized MnFe2O4 nanoparticles for sensitive detection of ascorbic acid
Release time:2025-11-19 Hits:
- DOI number:10.1016/j.snb.2025.137399
- Journal:Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical
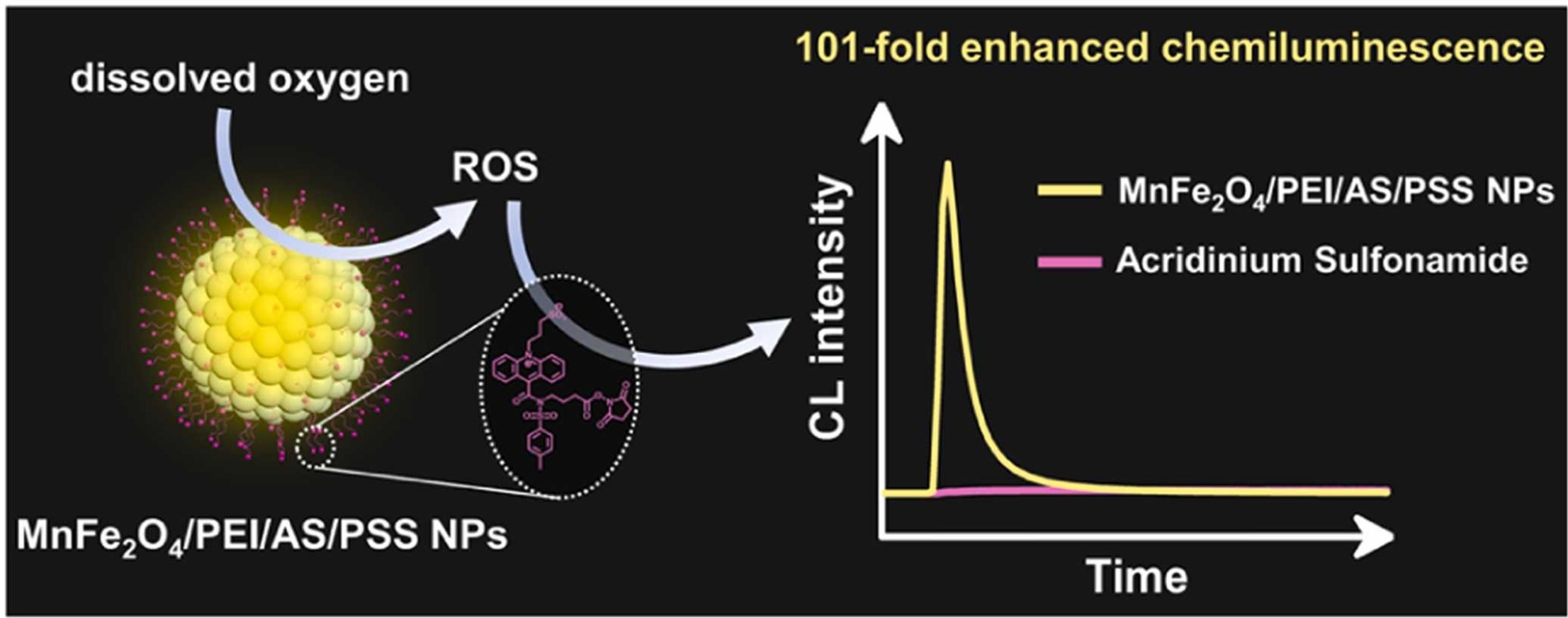
- Abstract:The development of efficient chemiluminescence (CL)-functionalized nanomaterials that use dissolved oxygen as a coreactant for analytical sensing remains a significant challenge. In this study, we present the synthesis of novel acridinium sulfonamide (AS)-functionalized MnFe2O4 nanoparticles, denoted as MnFe2O4/PEI/AS/PSS NPs, utilizing polyethyleneimine (PEI) as a bridge and poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate) (PSS) as a stabilizer. These MnFe2O4/PEI/AS/PSS NPs exhibited strong CL emission with the dissolved oxygen as a coreactant in the presence of hexadecyltrimethylammonium hydroxide (CTAOH). This enhanced CL performance was attributed to several factors: the large specific surface area and abundant amino groups on the MnFe2O4/PEI NPs, which enabled high AS loading efficiency; the catalytic activity of surface-bound Mn2 + and Fe2+ ions in generating reactive oxygen species from dissolved oxygen; and the positively charged micelles formed by CTAOH, which enriched superoxide anions. Additionally, PSS protects the excited state of N-(3-sulfonate-propane)acridone from environmental quenching, extending its lifetime and enhancing CL emission. Moreover, the MnFe2O4/PEI/AS/PSS NPs also demonstrated exceptional magnetic performance and stability. Based on this, a sensitive CL method for ascorbic acid (AA) detection was developed using MnFe2O4/PEI/AS/PSS NPs as a detection platform, without the requirement for recognition elements. The detection range was 0.08–200 µM with a low detection limit of 0.0714 µM. This method is rapid, simple, environmentally friendly, and stable, as it eliminates the need for an incubation process and additional coreactants. The CL method was effectively employed for the detection of AA in human serum samples, highlighting its potential for clinical diagnosis applications.
- First Author:胡超
- Co-author:聂威,王依莎
- Indexed by:Journal paper
- Correspondence Author:shujiangnan,Hua Cui
- Discipline:Natural Science
- Document Type:J
- Volume:431
- Page Number:137399
- Translation or Not:no
- Date of Publication:2025-05-15
- Included Journals:SCI
- Links to published journals:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925400525001741